Budgeting for Privacy Compliance
If you are thinking about budgeting for privacy compliance or how to control the costs of privacy compliance this article is for you. There are 4 major categories of expenses for the privacy compliance budget. These costs are those associated with the business process required to enable and operate a privacy program.
This is not an article about fines for GDPR, CCPA, LGPD or PEPIDA violations. or the lawsuits that individuals can potentially raise against businesses. It is also not a discussion of the security program budget. Privacy program costs can be categorized and controlled. These categories are described below including the levers that businesses have to control costs and strategies to minimize cost. If you are concerned about managing the budget for privacy operations (PrivacyOps), read on.
The diagram below shows the inter-related lifecycle of a full cybersecurity/privacy program. The PrivacyOps components are on the right side of the diagram.
The 4 major cost categories of PrivacyOps include:
- Data Mapping
- Managing Consent
- Building and Maintaining a Data Subject Request (DSR) workflow
- Responding to DSRs
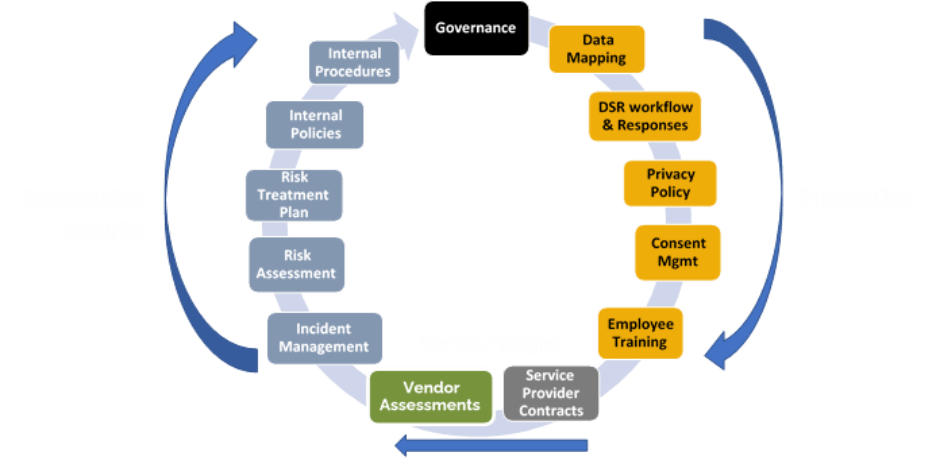
Businesses need to understand these cost categories to budget and to minimize expense. Businesses can control some activities that impact PrivacyOps costs including changes to the marketing program, business applications, data storage, PrivacyOps tools and employee costs. Other changes that affect cost cannot be controlled by the business. These include changes to privacy law the volume of DSRs received, but the business can modify how it responds to those changes and minimize the budgetary impact. There are three additional categories of costs associated with Privacy programs that are typically placed in other budgets. These are the information security program costs; the cost of managing privacy contractual requirements of service providers or data processing, auditing service provider security and privacy program adequacy and privacy program legal counsel expenses.
What are the 4 PrivacyOps budget categories?
Data Mapping
Data mapping is the activity of identifying what personal information (PI) is collected, how it is classified, why it is collected, where it is stored, how it moves within the organization or shared with third parties. Data Mapping is important because it identifies the assets that need to be protected, who owns it, how to find and manage it, when, why and how it is shared with third parties. Data maps need to be kept current. Data mapping effort can be a significant budgetary expense. Classically, the cost of data mapping is one of the largest initial privacy program costs. If not kept current, the expense to update them can be sudden and expensive. For example, many organizations found they needed to update their data maps when the European Court of Justice made the Schrems II decision. This forced companies to re-examine the flow of all EU resident personal and sensitive information to the US. Data mapping budgetary costs include:
- Classification of PI stored in every data source
- Documenting the purpose of collected PI
- Documenting the flow of PI across assets and third parties
Managing Consent
Why is there budgetary expense for managing consent? Laws like GDPR, PEPIDA and LGPD require that organizations get explicit consent from individuals before collecting and processing their personal information. Getting re-consent can be a requirement if the purpose of use changes or is expanded. This is true if the use and purpose changes for business applications, e.g, the marketing team begins to use PI associated with transactions to market. It is also true for PI collected to optimize the consumer’s experience on websites and mobile apps.
- There is a cost to record consent for new users and consent when purpose changes
- There is a cost to capture consent from visitors or users for data captured by third party components of websites and mobile apps.
Building and maintaining a DSR workflow
Privacy laws define the rights that consumers or residents have for their personal information. The DSR workflow defines the steps that are performed to:
- collect data subject information
- verify the identity of the requestor
- act on the request
- communicate with the requestor
- record the action taken
The budgetary components of building and maintaining a DSR workflow include:
- The employee time cost to document internal processes and data assets.
- Licensing cost for tools that support data discovery, workflow and robotic automation of DSRs
- Engineering cost to configure DSR workflow tools
- The number of data assets (where PI is stored) and whether the data assets hold structured data, e.g, databases or unstructured data, e.g., file storage or email systems
Responding to DSRs
Depending on the legal compliance requirements of an organization, there are up to four data subject request types, each with different cost impact to the business:
- Access requests – These requests require the organization to search for PI across within each asset that could contain the individual’s PI. The cost of responding to the request will depend on the number of business managed data assets, whether the asset has discrete records of personal information, e.g. a database or if it is unstructured like email and files in folders.
- Do Not Sell Requests – The cost will depend on how Do Not Sell Requests are implemented
- Correction requests – The cost will typically relate to the cost of the resource that acts on the request
- Delete/erasure requests – Delete requests are Access requests with special handling requirements. These requests can be the most expensive requests to process because businesses often need to make decisions on whether they have legitimate business reasons or legal requirements to keep the PI. And if they need to act on the delete request, cost could be low if applications can be used to delete the data quickly. Cost increases if the requestor’s PI is stored in PDF documents, emails or other unstructured documents where de-identification or redaction of specific lines needs to be done.
Strategies to minimize the cost of PrivacyOPs
Overall PrivacyOps Program Budgetary Strategy
Organizations are expected to implement compliance programs in a way that is reasonable to the organization, to its customer and to third parties, e.g. consumers. This implies that organizations do not need to boil the ocean as a first step in their compliance journey. Using this approach, we recommend that organizations consider an iterative approach to implement and continuously improve their PrivacyOps program. This approach allows businesses to manage cost with “reasonable” budget expenditures over time. Implementing and improving a privacy program in this way requires a risk management methodology and governance that can actively demonstrate that the interests of the company, its customers and others are in balance.
Data Mapping
Manual data mapping is costly because it is done by the most expensive people in the organization and if not managed, PI is stored in many locations including email. Businesses can reduce cost by reducing the data needing to be mapped:
- Eliminate unnecessary PI data repositories – Simplify applications and infrastructure to reduce the number of data assets, e.g., move to cloud-based file storage and eliminate redundant local file storage. This also reduces IT operations and security costs.
- Implement Privacy-by-Design rather than retrofitting processes, applications and data repositories after the fact.
- Employ automation for data mapping or data discovery to identify changes in data repositories, flow and collected PI rather than doing this manually. While data mapping can be straightforward for structured data repositories, it is very difficult for unstructured data such as email and file based repositories like OneDrive, SharePoint or Google Drive.
Managing consent
- Minimize third party cookies – this reduces effort to manage the purpose of each cookie in the cookie banner. Many sites have hundreds of cookies. Use a cookie banner application that automatically manages purpose and categorization
- Deploy a universal consent application, associated cookie banner and optional application consent forms. This eliminates the cost of building and maintaining a solution.
Building and Maintaining a DSR workflow
- Deploy a webform to capture DSR requests rather than use email or telephone calls that require that employees to transition the request to a workflow tracking system.
- Evaluate people time vs automation cost. Prioritize cost minimization effort DSR response activities where the most expensive internal resources need to be involved.
- Unstructured data resources have the highest complexity and likely benefit from automation.
Responding to DSRs
- Measure the expense of responding to DSRs for each workflow step and data source.
- Minimize PI within existing data repositories – If the business doesn’t have it, effort to respond is minimized. Maintain only PI for which there is a legitimate business purpose and keep only for the retention period defined by business policy. Limiting use and managing retention periods is also required by some privacy laws including GDPR and CPRA.
- Identify opportunities to reduce effort by shifting work to less expensive resources and automating DSRs.
- On a regular basis and as part of the step-based improvement process, look for changes that can move DSR requests to lower cost resources, possibly including complete automation.
Assured SPC understands the opportunities to minimize cost of privacy compliance programs. We bring 360-degree knowledge of privacy compliance, IT governance, cybersecurity, application development, website and infrastructure management, and process re-engineering to how we approach privacy compliance. Please feel free to reach out to us to discuss your situation or explain the content of this article.
Here is another page that you might find useful: Security vs Privacy,
Our Services
MANAGE - Virtual Chief Information Security Officer services
Contact us when you need a holistic but reasonable security program that addresses risk to the business not just technical controls. Click here for our virtual CISO services.
ASSESS -Privacy and Security program assessments
Contact us to understand the privacy and information risk posture of your organization. We translate information security into business terms.
DO - Implement and Operate your CCPA Privacy program
With our expertise in IT leadership, Security and Privacy, we can help you operationalize the California Consumer Privacy Act, reduce cost of implementation and operation and help you implement “reasonable security”. Check out our Operationalize CCPA Service
PREPARE - SOC 2 Readiness Management
We help organizations prepare for HIPAA, SOC 2, HITRUST and ISO27001 audits and to implement procedures and record keeping to maintain certification.
TEST - Security Testing and Remediation
We deliver Penetration and Vulnerability tests and help remediate issues